Understanding Risk to Reward Ratios in Trading: The Good vs. The Bad
Quick Information:
Check out our Trades
Join the Sniper Team
In trading, one of the most critical concepts to master is the risk to reward ratio. This ratio helps traders assess potential profit versus potential loss on a trade, guiding them in making informed decisions. A good risk to reward ratio can lead to consistent profitability, while a bad one can result in significant losses over time. In this blog, we'll explore the importance of risk to reward ratios, what constitutes a good vs. a bad ratio, and how to implement this into your trading strategy.
What is Risk to Reward Ratio?
The risk to reward ratio is the comparison between the amount of risk a trader is willing to take on an investment relative to the potential profit. It is usually expressed as two numbers, such as 1:3 or 1:2, where the first number represents the risk and the second number represents the reward.
- Risk: The amount you stand to lose if your trade goes against you.
- Reward: The amount you stand to gain if your trade works in your favor.
Why is Risk to Reward Ratio Important?
1. Capital Preservation: The primary goal of any trader should be to protect their capital. A favorable risk to reward ratio helps ensure that even if you experience a few losses, your profits from winning trades can more than compensate for those losses.
2. Emotional Control: Knowing your risk to reward ratio ahead of time can help you approach trading with a disciplined mindset. It reduces emotional decision-making and encourages adherence to your trading plan.
3. Long-Term Success: By maintaining a good risk to reward ratio, you can improve your chances of long-term profitability. This approach emphasizes quality over quantity—winning bigger on fewer trades rather than risking more for potential minimal gains.
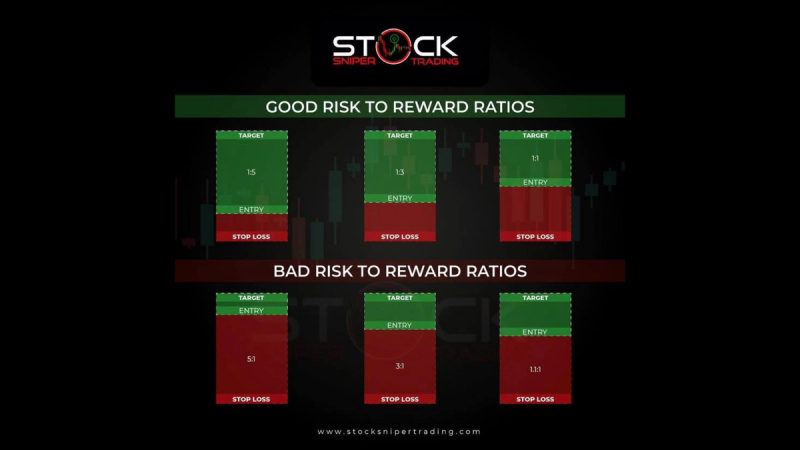
Good Risk to Reward Ratios
A good risk to reward ratio is often considered to be 1:2 or greater. Here’s what it typically entails:
1. 1:2 Ratio: For every dollar you risk, you aim to make two dollars. This is a common benchmark for many traders because it allows for losses to occur without devastating your trading capital.
2. 1:3 Ratio or Higher: Many successful traders aim for even higher ratios, such as 1:3 or 1:4. This means that for every dollar risked, the potential reward is $3 or $4. Such ratios can help traders remain profitable in the long run, even if their win rate is 50% or less.
3. Example: If you enter a trade with a stop-loss (risk) of $100 and a target profit (reward) of $300, you have a 1:3 risk to reward ratio. If you win this trade, your profit outweighs the loss from two losing trades based on the same risk amount.
Bad Risk to Reward Ratios
A bad risk to reward ratio can lead to detrimental outcomes for traders. Here’s what to be aware of:
1. 1:1 Ratio: A risk to reward ratio of 1:1 means that for every dollar risked, you only stand to gain one dollar. This can be problematic because it does not provide enough cushion for losses; experiencing a series of losing trades can quickly eat away at your capital.
2. Less than 1:1 Ratio: Ratios worse than 1:1 (like 1:0.5) indicate that you risk more than you stand to gain. This is an unsustainable strategy that can lead to accelerated losses in a trading account.
3. Example: If you risk $100 but only aim for a $50 gain, your risk to reward ratio is 1:0.5. If you encounter several losses, you’ll find that your capital diminishes rapidly, making recovery difficult.
How to Evaluate and Implement Risk to Reward Ratios
1. Set clear targets: Before entering a trade, determine your exit points based on prior support and resistance levels, moving averages, or other technical indicators.
2. Calculate your ratios in advance/ Clearly outline your entry point, stop-loss, and take-profit levels. By calculating the risk to reward ratio before executing a trade, you can ensure it meets your trading strategy criteria.
3. Adopt the right mindset: Accept that not every trade will be profitable. A good risk to reward ratio allows you to stay afloat even in the face of losses. Focus on being consistent rather than fixating on immediate outcomes.
4. Continuous evaluation: Regularly review past trades to evaluate your risk to reward ratios. This practice will help you identify patterns, adapt to market conditions, and refine your strategy over time.
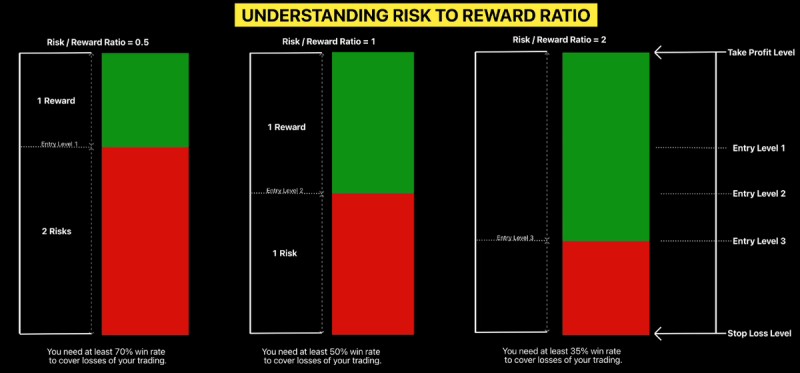
Understanding Risk to Reward Ratio:
Conclusion
Understanding risk to reward ratios is fundamental to successful trading. By distinguishing between good and bad ratios, traders can preserve capital, manage risk effectively, and increase their chances of long-term profitability. Implementing a disciplined approach toward risk management will not only enhance your trading performance but will also empower you to navigate the often volatile landscape of the financial markets with confidence.
Happy trading SST!

