Mastering Trading: The Five Fundamental Pillars
Trading can be both exhilarating and daunting, with the financial markets presenting opportunities and risks in equal measure. Whether you're a novice or an experienced trader, understanding the most critical aspects of trading can significantly influence your success. Here we delve deeper into five essential topics that form the foundation of effective trading.
1. Risk Management
Brief: At its core, trading is about managing risk while pursuing returns. Without a solid risk management plan, traders expose themselves to significant financial losses.
Effective risk management starts with setting clear loss thresholds. Stop-loss orders, for instance, are essential tools that automatically sell a security when its price falls to a predetermined level, thereby limiting potential losses. Diversification is another key strategy, involving the allocation of investments across various financial instruments, industries, or other categories to reduce exposure to any single asset or risk.
Position sizing is also crucial; it determines how much capital to allocate to a single trade based on your risk tolerance. Regularly assessing and adjusting your strategies ensures they remain effective under changing market conditions. Monitoring risk reward ratios—understanding potential gain versus potential loss—helps maintain balanced trading decisions.
2. Technical Analysis
Brief: Technical analysis is the study of past market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements.

Technical analysis hinges on the belief that historical trading activity and price changes of securities can be valuable indicators of future price movements. Chart patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangles provide visual cues about potential market direction.
Indicators like moving averages smooth out price data to identify trends over specific time frames, while RSI (Relative Strength Index) indicates whether an asset is overbought or oversold. The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is instrumental in identifying changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a security’s price. To maximize technical analysis effectiveness, it is essential to integrate multiple indicators to confirm signals and make informed trading decisions.
3. Trading Psychology
Brief: Trading psychology refers to the emotions and mental state that dictate a trader’s actions and influence decision-making processes.

Emotions play a significant role in trading, often leading to irrational behaviors that can derail even the most well-thought-out strategies. Recognizing and managing emotions like fear, greed, hope, and regret is key to maintaining discipline.
Traders should develop a robust trading plan and adhere to it, ensuring decisions are made based on strategy rather than emotion. It’s crucial to cultivate patience, understanding that trading involves both winning and losing trades. Accepting losses as part of the process and maintaining a balanced view helps preserve psychological capital. Consistently reviewing past trades can also provide insights into emotional triggers and help refine future behaviors.
4. Fundamental Analysis
Brief: Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a security's intrinsic value by examining related economic and financial factors.
This type of analysis digs deep into financial statements, earnings reports, and economic indicators to assess the worth of an investment. For stocks, this might involve analyzing a company’s revenue, profit margins, and debt levels, along with management effectiveness and market competition.
Economic indicators such as GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, and inflation can affect market dynamics, making them critical for traders to monitor. Additionally, industry trends and geopolitical events can also influence market perceptions and valuations. Successful fundamental analysis requires a holistic view, combining various data points to assess the underlying value of investments.
5. Trading Strategies
Brief: Trading strategies define the methodology and rules a trader follows to make investment decisions.
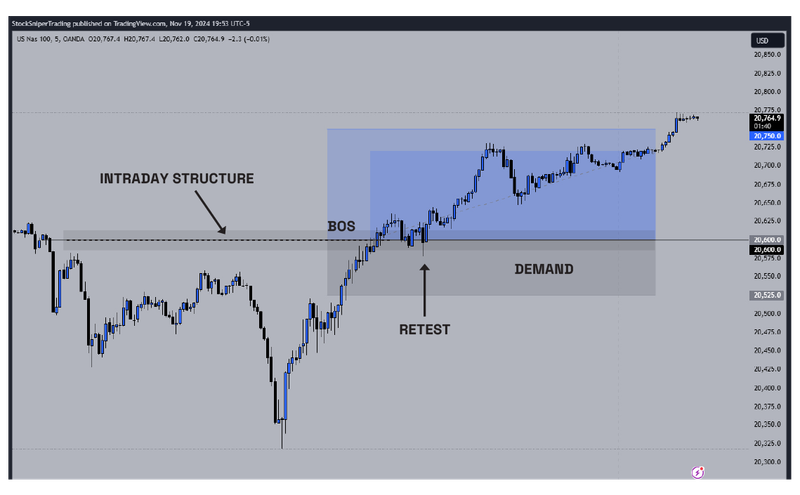
A trading strategy acts as a trader’s blueprint, providing a structured approach to navigating the market. Day trading involves making numerous trades over a single day, aiming to capitalize on small price movements. This strategy requires keen focus, quick decision-making, and comprehensive market knowledge.
Swing trading targets capturing profits from market movements over days or weeks and is suitable for those who want to avoid spending hours in front of a screen. Trend following strategies involve identifying and trading in the direction of market trends and are often used with long-term investments.
Each strategy comes with its own set of risks and rewards, requiring traders to choose and adapt strategies based on their goals, risk appetite, and market conditions. Periodic evaluation and adjustments are necessary to align with changing market dynamics and personal growth in trading skills.
In conclusion, mastering these five key topics—risk management, technical and fundamental analysis, trading psychology, and developing robust strategies—is crucial for achieving success in the markets. Whether you're starting or looking to refine your skills, continuous learning and adaptation remain pivotal in the ever-evolving world of trading.

